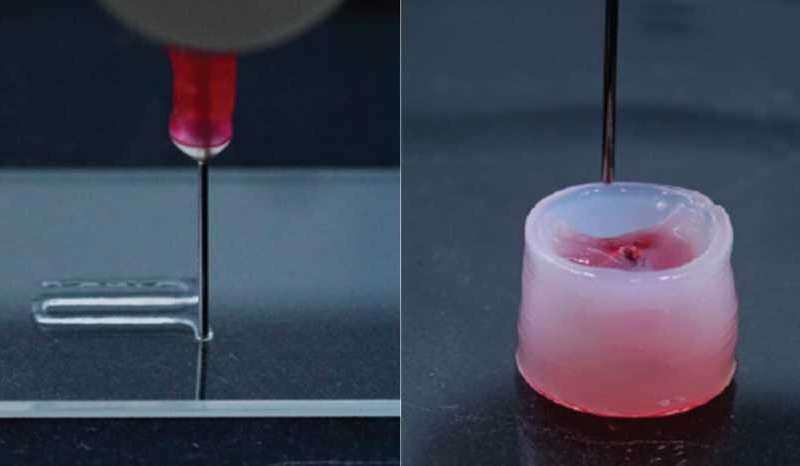
Researchers at ETH have produced a gel from cellulose
fibers and biodegradable nanoparticles that liquefies when pressed
through the nozzle of a 3-D printer, but then quickly returns to
its original shape. Their invention paves the way for personalized
biomaterial implants.