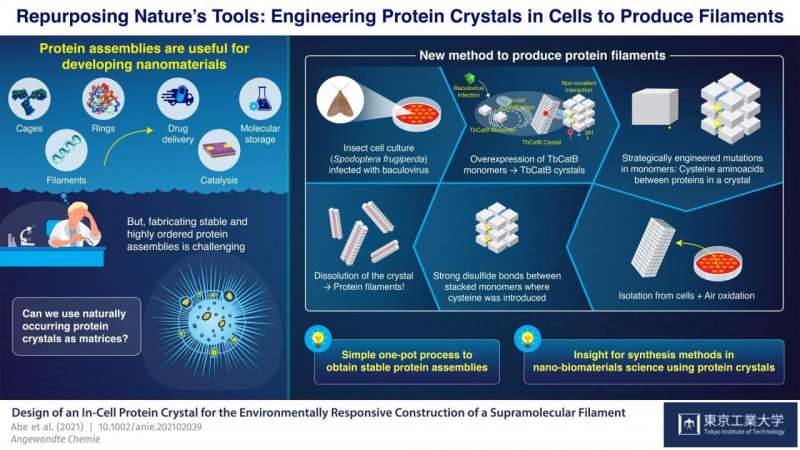
Proteins are undoubtedly some of the most fascinating
biomolecules, and they perform many of the functions that (in our
eyes) separate life from inanimate matter. Multi-molecular protein
assemblies even have large-scale structural functions, as evidenced
by feathers, hair, and scales in animals. It should come as no
surprise that, with progress in advanced nanotechnology and
bioengineering, artificial protein assemblies have found
applications in a variety of fields, including catalysis, molecular
storage, and drug delivery systems.
In-cell nano-3D printer: Synthesizing stable filaments from
in-cell protein crystals