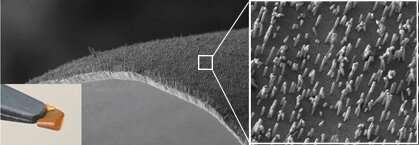
Knowing the state of mammalian cells, in particular
neural cells, depends on advances in nanotechnology‐based
interfaces. Nanotechnology offers new technical possibilities to
unravel the connectivity routes of the nervous system by adding
nanoscale features for a more intimate interface with neurons. In
this regard, non-invasive microelectrodes of improved design and
low impedance are highly desired. So far flexible electrodes have
been proposed, but only a few combine flexibility with both
nanostructure and a low impedance.