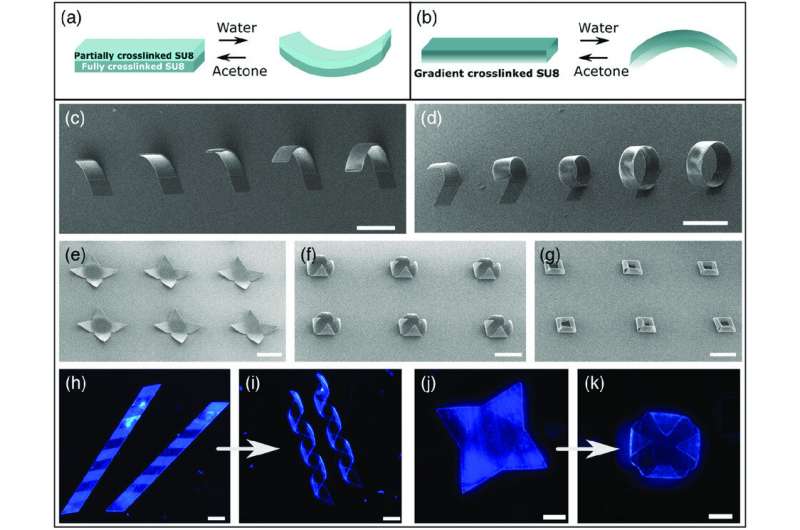
Stimuli-responsive, self-folding, two-dimensional
(2-D) layered materials have interesting functions for flexible
electronics, wearables, biosensors, and photonics applications.
However, limits with scalability and a lack of design tools can
prevent high integration and their reliable function. In a new
report now published on Advanced Intelligent Systems, Qi Huang, and
a team of scientists in chemical and biomolecular engineering and
electrical and computer engineering at Johns Hopkins University,
U.S., proposed a mass-production strategy to create monolayer
graphene-based reversible self-folding structures. The material can
be used in microfluidics and micromechanical systems. As proof of
concept, they achieved complex and functional devices in the form
of rings, polyhedra, flowers and origami birds. They then
integrated gold electrodes to the constructs to improve their
detection sensitivity. The experiments suggest a comprehensive
framework to rationally design and fabricate scalable and complex,
3-D, self-folding optical and electronic devices by folding 2-D
monolayer graphene.