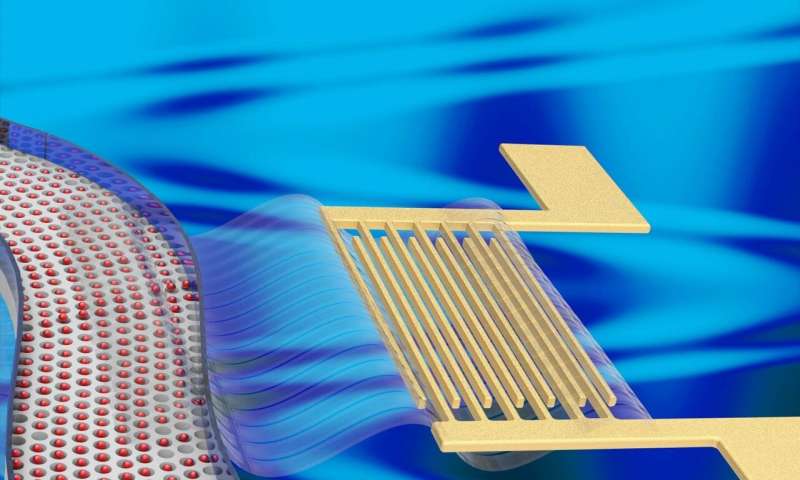
Acoustofluidics is the fusion of acoustics and fluid
mechanics that provides a contact-free, rapid and effective
manipulation of fluids and suspended particles. The applied
acoustic wave can produce a non-zero time-averaged pressure field
to exert an acoustic radiation force on particles suspended in a
microfluidic channel. However, for particles below a critical size
the viscous drag force dominates over the acoustic radiation forces
due to the strong acoustic streaming resulting from the acoustic
energy dissipation in the fluid. Thus, particle size acts as a key
limiting factor in the use of acoustic fields for manipulation and
sorting applications that would otherwise be useful in fields
including sensing (plasmonic nanoparticles), biology (small
bioparticle enrichment) and optics (micro-lenses).
Scientists lead development of novel acoustofluidic
technology that isolates submicron particles