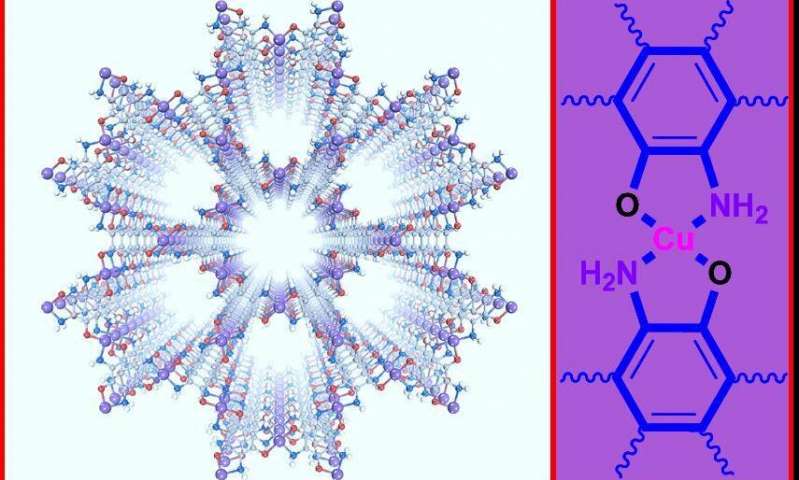
Metal-organic frameworks, or MOFs, are composed of
metal ions periodically surrounded by organic bridging molecules,
and these hybrid crystalline frameworks feature a cage-like hollow
structure. This unique structure motif offers great potential for a
range of applications in energy storage, chemical transformations,
optoelectronics, chemiresistive sensing, and
(photo)electrocatalysis, among others. Debuted in the early 2000s,
MOFs are a fascinating nanomaterial. Though numerous applications
exploit MOFs, little has been known as to how oxygen may work in
the synthesis of MOFs.