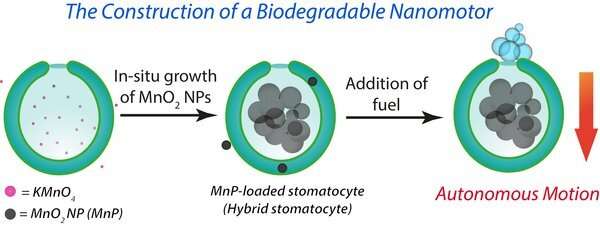
Nanomotors are molecular or nanoscale devices that can
move through a biological medium by converting chemical energy into
motion, and can be used for the delivery of pharmaceutical drugs to
specific parts of the body. Typically, nanomotors use biomolecules
for propulsion. However, these molecules can suffer degradation
when in the body. Researchers from the Institute for Complex
Molecular Systems (ICMS) at Eindhoven University of Technology
(TU/e) along with researchers from Soochow University, Swansea
University, and the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia
(IBEC) have developed a new hybrid approach for biodegradable
nanomotors where inorganic nanoparticles stored in the nanomotors
help to propel the nanomotors. This study has been published in the
journal Nano Letters.
New ‘hybrid engine’ for biodegradable nanomotors that
transport drugs to diseased tissue