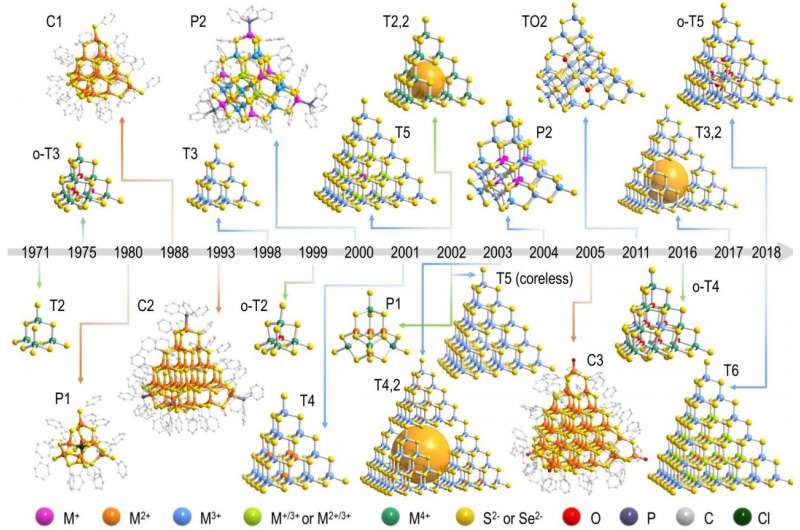
Nanoclusters, which consist of several or even
thousands of atoms, represent an important intermediate state
between microscopic atoms and macroscopic matter. A profound
comprehension of the composition, structure, and properties of
nanoclusters is crucial for exploring or extending their functional
applications. Among the numerous types of nanoclusters, metal
chalcogenide supertetrahedral clusters (MCSCs) have attracted great
attention since the 1980s for their uniform sizes, well-defined
structures, and semiconductor properties. Notably, because of their
resemblance to II-VI or I-III-VI semiconductor nanocrystals (also
known as quantum dots, QDs), MCSCs have been regarded as atomically
precise ultrasmall QDs and used to clarify various issues that
could not be resolved using traditional QDs, such as the
determination of precise site-dependent structure-property
relationships.
Insights into construction of metal chalcogenide
supertetrahedral clusters