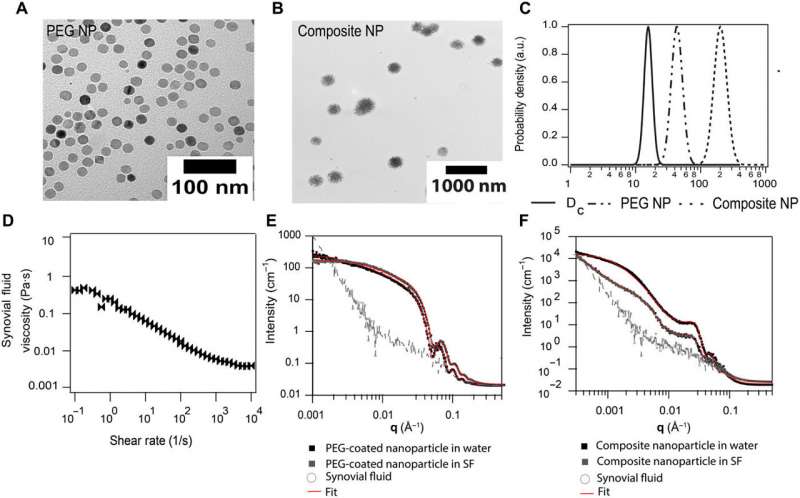
Nanoparticles have applications as therapeutic agents
for joint diseases such as osteoarthritis. But the role of
nanoparticle diffusion in synovial fluid or the fluid inside the
joint is incompletely understood. In a new report now published on
Science Advances, Mythreyi Unni and a research team in chemical
engineering and biomedical engineering in the U.S. used the
Stokes-Einstein relationship to describe the rotational and
translational diffusion of polymer-coated nanoparticles in
quiescent synovial fluid and hyaluronic acid solutions. The
outcomes provided insight to the diffusive behavior of
polymer-coated inorganic nanoparticles in complex aggregates of
biological environments that are typically present in the
joint.
Fast nanoparticle diffusion in synovial fluid and hyaluronic
acid solutions