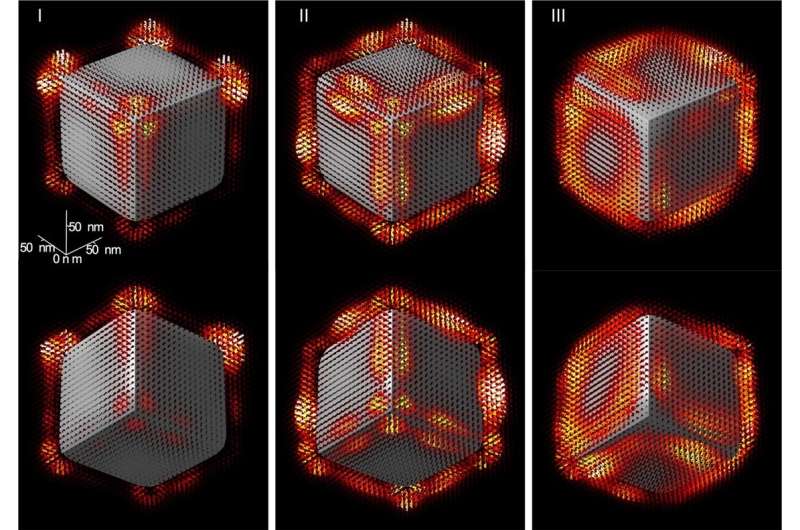
Imagine a cube on which light is projected by a
flashlight. The cube reflects the light in a particular way, so
simply spinning the cube or moving the flashlight makes it possible
to examine each aspect and deduce information regarding its
structure. Now, imagine that this cube is just a few atoms high,
that the light is detectable only in infrared, and that the
flashlight is a beam from a microscope. How to go about examining
each of the cube’s sides? That is the question recently answered by
scientists from the CNRS, l’Université Paris-Saclay, the University
of Graz and Graz University of Technology (Austria) by generating
the first 3D image of the structure of the infrared light near the
nanocube. Their results will be published on 26 March 2021 in
Science.