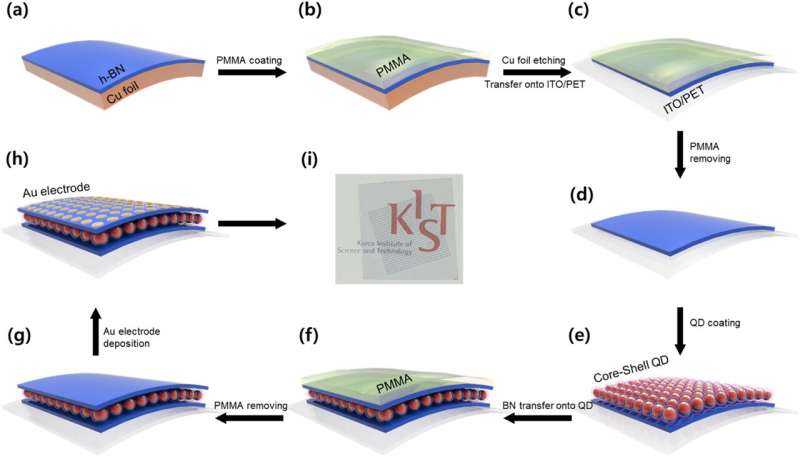
A two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterial-based flexible
memory device is a critical element in the next-generation wearable
market because it plays a crucial role in data storage, processing,
and communication. An ultra-thin memory device materialized with a
2D nanomaterial of several nanometers (nm) can significantly
increase the memory density, leading to the development of a
flexible resistance-variable memory with the implementation of a 2D
nanomaterial. However, memories using conventional 2D nanomaterials
have limitations owing to the weak carrier trapping characteristics
of the nanomaterials.