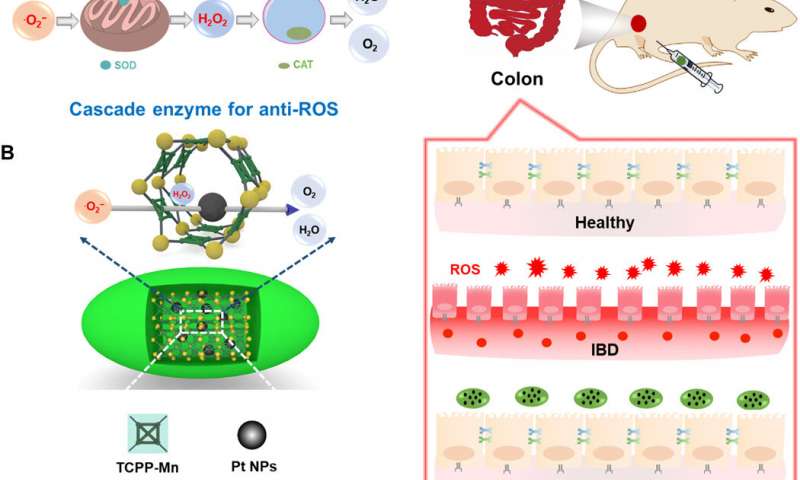
In a recent report, Yufeng Liu and a team of
interdisciplinary researchers in China developed an integrated
nanozyme cascade to eliminate excessive reactive oxygen species
(ROS; oxygen free radicals). The nanozyme mimicked superoxide
dismutase (a group of enzymes) and incorporated a manganese
(Mn)-based metal-organic framework (MOF) to transform oxygen
radicals to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Using in-lab and in vivo
experiments, the team showed the ROS-scavenging potential of
integrated cascade nanozymes. As proof of concept, they relieved
two forms of inflammatory bowel disorder (IBD)—ulcerative colitis
and Crohn’s disease using cascade nanozymes as effective
treatments. The study provided a new method to construct
enzyme-like cascade systems and illustrate the promise of their
efficient therapy to treat IBD in vivo. The work is now published
on Science Advances.
Designer nanozymes for reactive-oxygen species scavenging
anti-inflammatory therapy