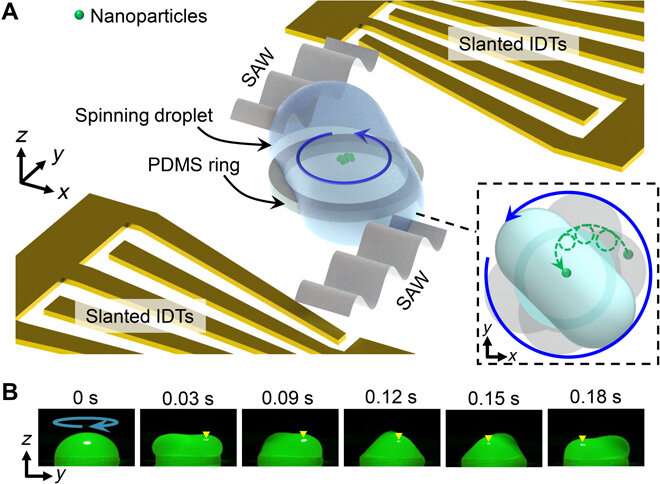
Liquid droplets have recently gained renewed attention
as a simplified model for a variety of fascinating physical
phenomena at the scale of the cell nucleus to stellar black holes.
In a new report now published in Science Advances, Yuyang Gu and a
team of scientists in the U.S. presented an acoustofluidic
centrifugation technique that used the entanglement of acoustic
wave actuation and the spin of a fluidic droplet to accomplish
nanoparticle enrichment and separation. They combined acoustic
scanning and droplet spinning methods to achieve rapid nanoparticle
concentrations and size-based separation with a resolution
sufficient to identify and isolate exosome
sub-populations.